Paper bags may look simple, but behind each one lies a carefully designed manufacturing process that blends natural raw materials with modern machinery. Every year, billions of paper bags are produced globally, with the paper bag industry growing due to rising demand for environmentally friendly packaging as businesses shift away from plastic bags.

From durable kraft paper to recycled fibers, the production of paper bags involves multiple steps, from preparing paper pulp to applying handles that ensure strength, quality, and eco-friendliness. Whether you’re a student curious about how are paper bags are manufactured or a retailer exploring paper bag manufacturers, this guide takes you inside the manufacturing process from start to finish.
Looking for sustainable packaging for your business? At Itendee, we provide custom paper packaging solutions. Contact us today!
What Are Paper Bags Made Of?
The strength and sustainability of paper bags depend on the raw materials used in producing paper bags. Different applications, from grocery sacks to luxury retail bags, require different grades of paper. Here are the most common materials used in manufacturing paper bags:
Kraft Paper
The backbone of the paper bag industry, kraft paper is made from wood pulp through a chemical pulping process that leaves long, durable cellulose fibres. This makes kraft paper from wood chips exceptionally strong, ideal for brown paper bags, grocery bags, and industrial paper bags used for heavy-duty applications like flour, cement, or animal feed. Its natural brown shade can be left as-is or bleached into crisp white paper.

Recycled Paper
For businesses seeking environmentally friendly packaging, recycled paper is one of the paper products that is a go-to option. Made from recycled materials such as used paper and cardboard, it helps reduce the environmental impact of bag production while meeting market demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Recycled paper is commonly used in shopping bags, gift packaging, and retail take-out bags.

Coated Paper Options
Some paper bags are made with coatings that provide resistance to grease, moisture, or wear. Wax-coated bags are popular in the bakery and food service industry for carrying cookies, sandwiches, or greasy items. Laminated paper may be used in luxury paper bags for durability and a premium finish, though excessive lamination can limit recyclability.

Specialty Papers
For high-end branding, specialty paper bags use textured, luxury, or colored paper. These are common in the retail industry, where brand colors, logos, and finishes make the packaging part of the overall customer satisfaction experience. Options include flat-bottomed paper bags, rope-handled luxury bags, or themed designs for promotions.

At Itendee, we use only the highest quality materials, from sturdy kraft paper to premium textured sheets, ensuring every bag balances durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. Explore our custom paper bag solutions to see how the right material can elevate your brand.

Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
At Itendee, every paper bag goes through a carefully managed sequence of steps to ensure it is functional, strong, and eco-friendly. While the process relies on advanced machines, it’s the attention to detail at each stage that makes the difference.
Step – 1: Paper Roll Preparation
The process begins with large rolls of kraft or recycled paper, which are the foundation of every bag. These rolls are loaded onto the machine’s unwinding unit, where they are aligned, tensioned, and cut to the required width. Proper alignment and tension control are critical; any misplacement at this stage can cause uneven folds, weak seams, or printing errors later in the process.
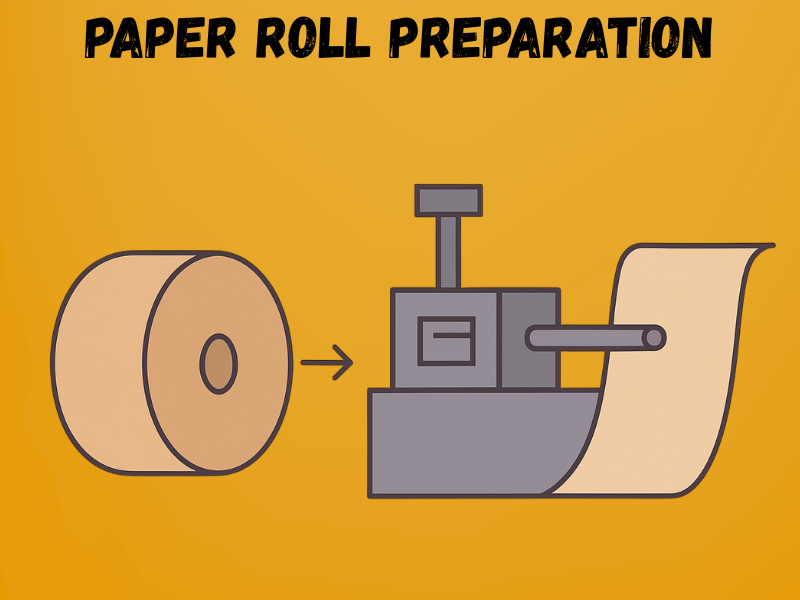
Key Details
- Roll width: Usually 600 mm – 1500 mm, depending on bag size.
- Roll diameter: Up to 1200 mm for high-volume runs.
- Paper thickness (GSM): Ranges from 35–120 GSM for grocery and retail bags.
- Machine controls: Auto-tension systems maintain even feeding.
Step – 2: Printing & Branding (Optional)
Before the paper is shaped into bags, it often goes through printing where logos, designs, or marketing messages are added. Flexographic printing using printing cylinders is most common for kraft paper because of its speed and versatility, while offset printing is used for sharper, high-resolution images. To stay eco-friendly, manufacturers prefer water-based or soy-based inks, which dry quickly, prevent smudging, and keep the bags recyclable, minimizing their environmental impact.
Key Details
- Printing width: Typically up to 1200 mm paper rolls.
- Ink type: Water-based or soy-based for sustainability.
- Printing methods: Flexographic (fast, cost-effective) or offset (high-quality graphics).
- Quality checks: Ink viscosity, color calibration, and alignment are monitored in real-time.
Step – 3: Tube Formation
Once the paper is prepared (and printed if required), it moves into the tube-forming section. Here, the flat sheet is folded into paper layers and glued along the edges to create a continuous paper tube. At the same time, gussets (side folds) are shaped to allow the bag to expand when filled. Precision is vital; any misalignment in folding or gluing can weaken the bag’s structure and impact its load capacity.
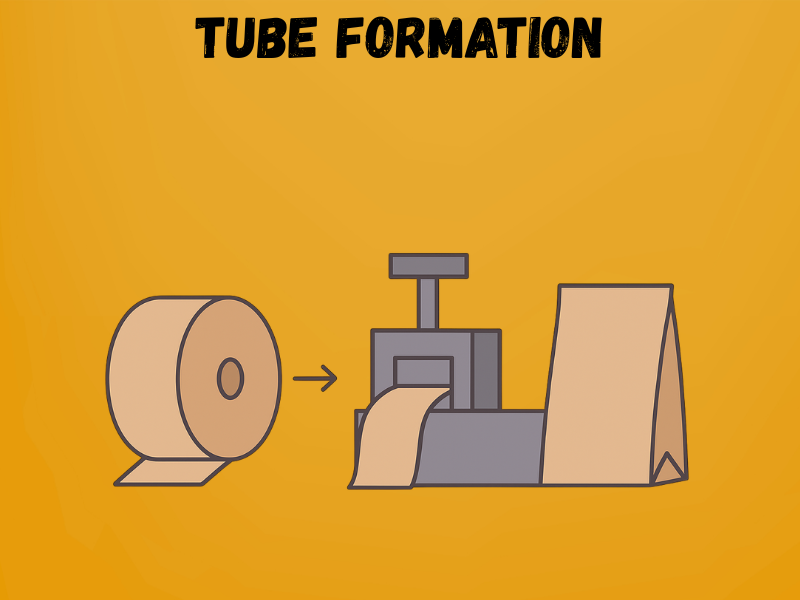
Key Details
- Folding type: Side gussets range from 30–120 mm, depending on bag style.
- Glue application: Water-based adhesives applied at 0.5–1 g per bag.
- Tube width range: Typically 150 mm – 600 mm.
- Machine speed: Up to 500 bags per minute in modern setups.
Step – 4: Bottom Formation & Gluing
After the tube is created, the machine forms the bag’s bottom. This step involves folding and gluing the lower edges to create a flat, secure base. Depending on the style, the bottom may be square (flat-bottom) for grocery and shopping bags, or pinch-bottom for simpler packaging. Strong adhesives ensure that the bottom can handle the intended load without tearing.
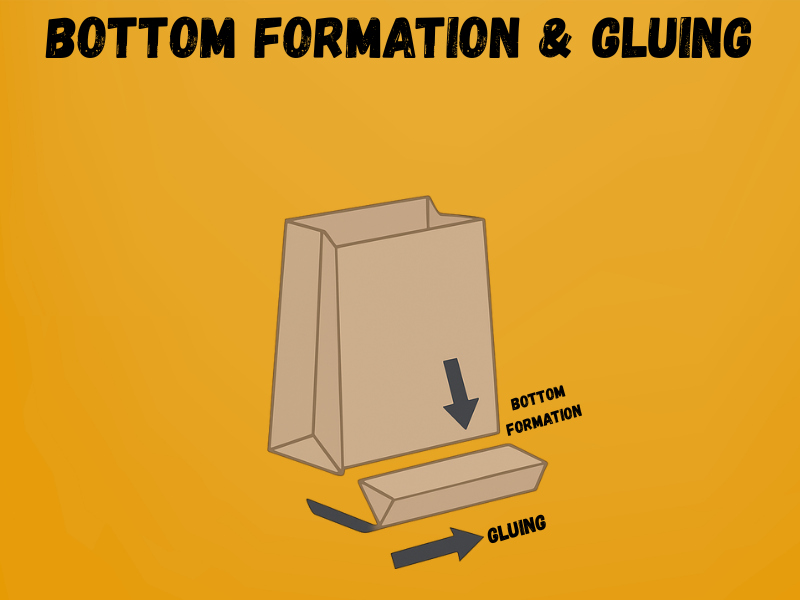
Key Details
- Bottom width: Ranges between 70 mm – 250 mm, depending on bag size.
- Folding precision: Alignment tolerance is usually within ±1 mm.
- Adhesive type: Water-based or starch-based glue, approx. 1–2 g per bag.
- Load capacity: Proper gluing allows bags to hold between 2 kg – 15 kg safely.
Step – 5: Cutting into Individual Bags
Once the tube and bottom are formed, the continuous paper roll is cut into individual bags. Precision cutters ensure each bag matches the required length while maintaining clean edges for folding and stacking. Any misalignment at this stage can lead to uneven bags, which are rejected during quality checks.
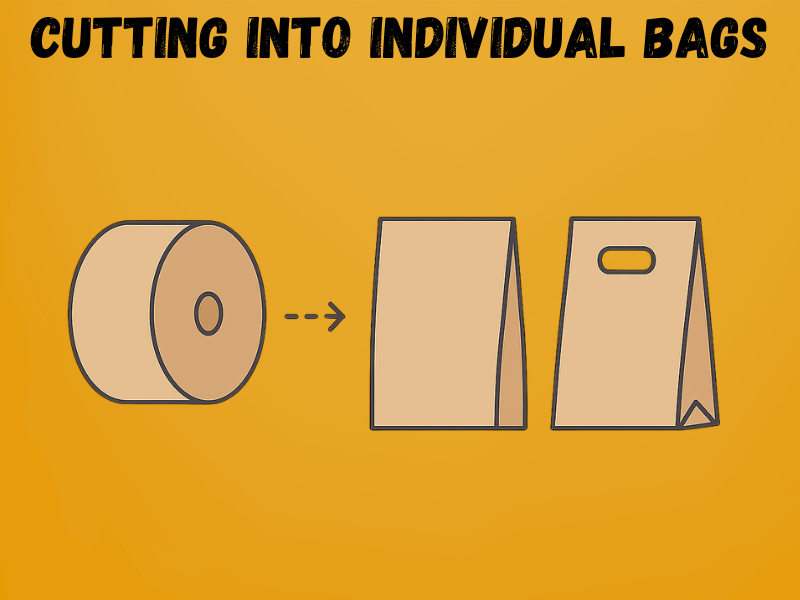
Key Details
- Bag length: Typically ranges from 150 mm to 600 mm, depending on design.
- Cutting speed: Modern machines cut up to 200–600 bags per minute.
- Tolerance: Accuracy is maintained within ±0.5 mm.
- Automation: Sensors track alignment and automatically stop the machine if paper shifts.
Step – 6: Handle Application (If Required)
For premium shopping and retail bags, handles are added to improve convenience and strength. Depending on the bag type, twisted paper handles, flat paper handles, or rope handles are attached using strong adhesives or reinforced patches. Placement accuracy is essential to ensure the bag can carry weight evenly without tearing.
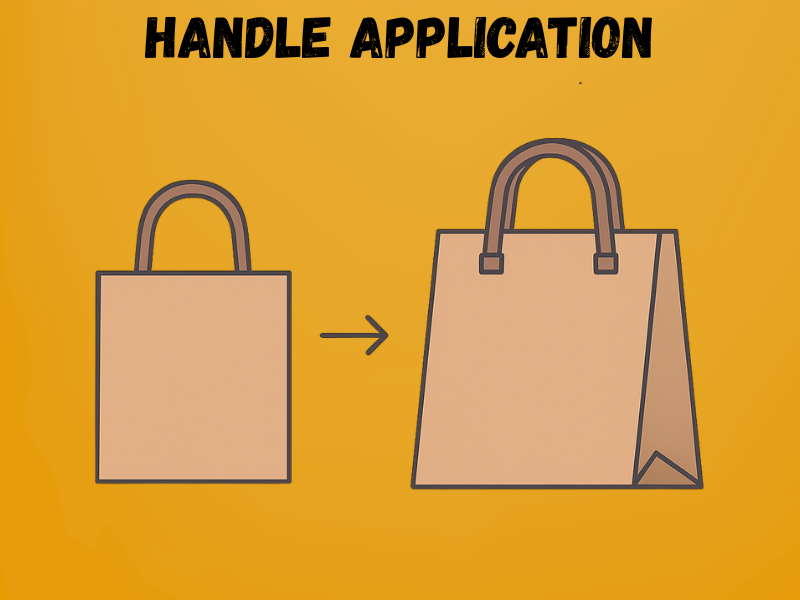
Key Details
- Handle types:
- Twisted paper (eco-friendly, lightweight use)
- Flat paper (stronger, for groceries or retail)
- Rope handles (luxury or premium bags)
- Attachment method: Hot-melt or water-based adhesives applied with reinforcement patches.
- Load capacity: Properly fixed handles can support 5–15 kg, depending on bag design.
- Automation: In modern factories, handle-making units are integrated into bag-forming machines for continuous, high-speed production.Step – 7: Drying & Quality Check
Step 7: Drying & Quality Check
Once the handles and glued seams are applied, bags go through a drying system to allow adhesives to set firmly. After drying, each batch undergoes strict quality checks to ensure strength, durability, and appearance.
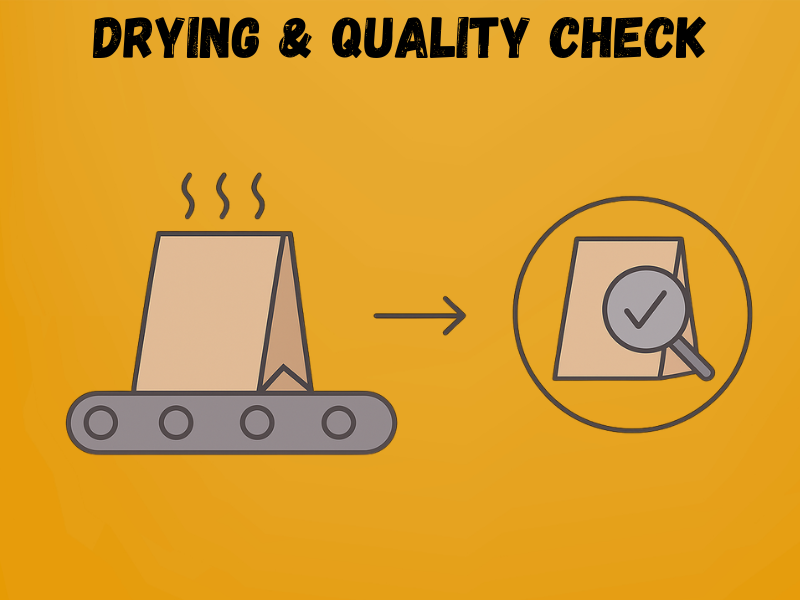
Key Details
- Drying methods: Conveyor belts with hot air or infrared heating speed up glue curing.
- Inspection points
- Handle pull strength
- Bottom seam integrity
- Folding and alignment accuracy
- Print clarity and color consistency
- Load testing: Random bags are tested to confirm they can hold their intended weight (e.g., 5–15 kg depending on design).
- Defect handling: Bags with misaligned folds, weak seams, or printing errors are recycled back into pulp instead of being wasted.
- Certifications & Food Safety StandardsHigh-quality paper bags often comply with international certifications, such as:
- FSC (Forest Stewardship Council): ensures paper is sourced from responsibly managed forests.
- ISO 22000 / FDA (for food-grade bags): guarantees bags are safe for direct food contact.
- EN 13432: certifies compostable bags meet EU environmental standards.
Step 8: Packing for Delivery
After passing quality checks, the finished paper bags are carefully packed for safe transport and delivery to clients. Proper packing ensures that the bags retain their shape and remain undamaged during handling.
Key Details:
- Bundling: Bags are counted and stacked in bundles (usually 50–100 bags per pack) for easier handling.
- Protection: Bundles are wrapped in shrink film or packed into corrugated cartons to prevent moisture, dust, or damage.
- Labeling: Each carton is labeled with size, style, GSM, quantity, and client order details.
- Storage conditions: Packed cartons are stored in dry warehouses with humidity control to prevent warping.
- Distribution: Depending on order size, bags are shipped via freight trucks, containers, or air cargo for export markets.
Common Defects & How They’re Handled
Defects such as weak glue application, uneven folds, or misprinted graphics are identified during batch checks. Bags that fail to meet quality standards are removed and recycled back into production, minimizing waste. Manufacturers maintain strict quality assurance systems to prevent defective bags from reaching retailers or end users, in order to lower carbon dioxide emissions.
Types of Paper Bags Manufactured
Paper bag manufacturing encompasses a wide range of products, from lightweight grocery carriers to premium retail bags and even heavy-duty industrial packaging. At a glance:
- Grocery bags focus on affordability and recyclability.
- Luxury bags highlight style, branding, and presentation.
- Food service bags emphasize safety and grease resistance.
- Industrial bags provide strength for bulk goods.
Let’s look at each type in more detail.
Brown Kraft Grocery Bags
Simple, durable, and recyclable, these bags are the everyday staple of the paper bag industry. Made from kraft paper, they come in flat-bottom and gusseted versions, perfect for groceries, books, or packed lunches. Their affordability and eco-friendly appeal make them the go-to choice for mass retail and daily use.

Luxury Paper Bags
Luxury bags combine function with presentation. Made from thicker or coated paper, they feature rope or ribbon handles, laminated surfaces, and high-quality printing. Used by fashion retailers, jewelry stores, and premium brands, they double as a packaging solution and a branding tool that customers often reuse.

Food Service Bags
These bags are designed for direct food contact, often featuring wax- or grease-resistant coatings. Bakeries and cafés use them for pastries, sandwiches, and takeaway meals. Printed with food-grade inks, they balance practicality with branding opportunities, ensuring safety while promoting eco-conscious packaging.

Multi-Wall Industrial Bags
Built to withstand weight and rough handling, multi-wall bags consist of several layers of kraft or recycled paper. They’re used for cement, flour, sugar, or animal feed, with reinforced bottoms that prevent tearing. Their heavy-duty design makes them indispensable in the packaging industry for bulk transport.
From simple grocery bags to premium luxury packaging, Itendee offers every style of paper bag your business may need.
Different Bag Styles & Finishes
Beyond their types and uses, paper bags are also distinguished by their structural styles and surface finishes. These variations determine how the bags perform, look, and feel in different settings.
Flat-Bottomed Paper Bags
These bags feature a stable, square bottom that allows them to stand upright. They are widely used in groceries, retail packaging, and takeaway food because they can hold more weight and prevent items from tipping.

Valve & Open-Mouth Bags
Common in the industrial packaging sector, valve bags are filled through a small valve opening and are perfect for powdered products like cement or flour. Open-mouth bags, on the other hand, have wide openings for easy filling and sealing.

End-Sealed & Pleated Side Bags
End-sealed bags are compact and often used for lightweight items, while pleated side bags expand with more volume, making them ideal for bulkier products.

Custom Finishes: Matte, Glossy, Textured, or Colored
Paper bags can be enhanced with various finishes. Matte and glossy coatings affect visual appeal, while textured and colored designs add luxury or branding value. Businesses often use custom finishes on multi-wall paper bags to align packaging with brand identity.

Stand out with Itendee’s customizable paper bag finishes, matte, glossy, textured, or colored, designed to match your brand identity.
Challenges in Paper Bag Manufacturing
Even though paper bags are eco-friendly and widely used, manufacturers face technical and operational challenges during production. Here’s a breakdown:
| Challenge | Impact on Manufacturing | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Quality | Low-quality recycled paper leads to weaker bags that tear easily. | Source higher-grade kraft/recycled paper, add starch or resin for reinforcement. |
| Moisture Sensitivity | Paper absorbs moisture, losing strength during storage or use. | Apply wax/lamination coatings or store paper in climate-controlled warehouses. |
| Ink Adhesion Issues | Poor ink adhesion causes blurred logos or fading prints. | Use water-based flexographic inks and pre-treated paper surfaces. |
| Machine Downtime | Frequent jams or misalignment slow down production. | Regular machine calibration, staff training, and preventive maintenance. |
| Handle Attachment Failures | Handles detach under heavy loads, leading to customer dissatisfaction. | Reinforce handle patches, use stronger adhesives, or automate handle application. |
| Bottom Seam Weakness | Bags split open when carrying heavy goods. | Double-fold bottom seams, apply stronger glue patterns. |
| Sustainability Pressure | Demand for eco-friendly certifications increases production costs. | Adopt FSC-certified sourcing, invest in recyclable coatings, and optimize waste recycling. |
Environmental Benefits of Paper Bag Manufacturing
Paper bags are more than just a packaging option; they represent a shift toward sustainability. Their production and disposal processes help reduce long-term environmental harm.

Renewable Raw Materials
Most paper bags are produced from wood pulp or recycled paper, which makes them a renewable alternative to plastic. Unlike petroleum-based plastics, paper relies on resources that can be replenished through responsible forestry and recycling programs.
Recyclable and Biodegradable
One of the strongest advantages of paper bags is their end-of-life cycle. They can be recycled multiple times and, if disposed of, they naturally biodegrade within weeks or months, unlike plastic products that take centuries. This reduces waste buildup in landfills and oceans.
Lower Carbon Footprint
The overall production and disposal of paper bags result in a lower carbon footprint compared to plastic bags. While paper manufacturing does require energy and water, the ability to recycle, compost, and reduce long-term pollution makes paper bags a more sustainable choice.
Switch to Itendee’s paper bags and reduce your carbon footprint with recyclable, biodegradable, and renewable packaging options.
FAQs – Paper Bag Manufacturing FAQ
Curious about how paper bags are made or what sets kraft paper apart? Here are some of the most common questions answered in simple detail.
What raw materials are used to make paper bags?
Paper bags are typically made from kraft paper, recycled paper, or specialty coated papers. Kraft paper is strong and durable, while recycled options support sustainability.
Are all paper bags recyclable?
Yes. Most paper bags are 100% recyclable and biodegradable, except for those with plastic film or heavy lamination.
What machines are used in making paper bags?
Modern production relies on bag-making machines, printing presses, handle applicators, and cutting equipment to produce consistent, high-quality bags.
How long does it take to make a paper bag?
With industrial machines, manufacturers can produce thousands of paper bags per hour, making it fast and scalable.
Why are Kraft paper bags stronger than regular paper bags?
Kraft paper goes through a special pulping process that leaves longer, tougher fibers, giving the bags higher strength and durability.
Final Thoughts!
The manufacturing of paper bags is a streamlined process that combines renewable raw materials, efficient machinery, and eco-friendly design. Whether it’s grocery sacks, food-service packaging, or luxury shopping bags, paper bags deliver both functionality and environmental benefits sustainably.
Choose Sustainable Paper Bags for Your Brand
Switching to eco-friendly packaging doesn’t just help the environment; it builds trust with your customers. At Itendee, we offer custom recyclable paper bags made tailored to your business, from kraft grocery bags to premium printed retail packaging.






